Textile And Printing Industry Wastewater
(2024年)https://www.jiuwumembrane.com/application/textile-and-printing-industry-wastewater.html
Dyeing Wastewater Treatment Technologies
Printing and dyeing sizing wastewater alkali reuse technology patent is the use of ceramic ultrafiltration membrane technology to concentrate sizing wastewater, which permeates directly backs to the sizing process, water and caustic soda are reused fully after treatment resulting in zero discharge. The technology has achieved industrial scale applications and access to a national invention patent.
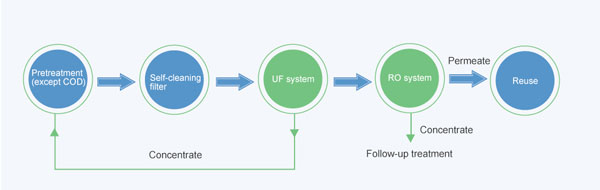
1. Dyeing and sizing wastewater contains a large amount of refractory slurry, the slurry into the sewage treatment system, increasing the difficulty of biochemical treatment, making sewage treatment costs increase. Printing and dyeing sizing wastewater also contains a higher concentration of caustic soda (0.5% ~ 7%) and a certain amount of refining agent, with a high recovery value.
2. Using uf membrane technology, the printing and dyeing sizing wastewater concentration treatment, membrane treatment of the permeate directly to the sizing process, including water and caustic soda, etc. can be completely reused to achieve zero discharge of sewage treatment.
Refined water from a dying plant in Nantong is treated by ceramic membrane technology, project design daily capacity is 500m3 or more, yield meets the workshop reuse requirements.
INDIGO RECOVERY
The dye wastewater containing indigo is characterized by a dark blue color due to the presence of the dye not fixed to the fiber during the dyeing process.
The primary use for indigo is as a dye for cotton yarn, which is mainly for the production of denim cloth for blue jeans.
The wastewater containing indigo is characterized by a moderate amount of chemical oxygen demand (COD), pH, suspended solids, dissolved solids and a dark blue color, due to the presence of the dye not fixed to the fiber during the dyeing process.
JIU WU HI-TECH utilizes the unique integrated membrane systems for dye wastewater treatment, which recover the insoluble indigo dye, the production of a secondary commercial product from the waste stream through a by-product synergy process offers an attractive alternative to discharging the untreated effluent into municipal treatment plants or the environment.
WASHING EFFLUENTS
Washing is a finishing process applied to fibres, yarns, and fabrics.
Washing is normally carried out in hot water (40-100°C) in the presence of wetting agent and detergent. The detergent emulsifies the mineral oils and disperses the undissolved pigments. The choice of the surfactants may vary also depending on the type of fibre. Mixtures of anionic and non-ionic surfactants are commonly used. An important factor in the selection of a surfactant is its effectiveness in strongly alkaline conditions.
Washing effluents are mainly composed of soap, grease, synthetic detergents, detergents and a small amount of bacteria, coliform bacteria, viruses, and other harmful substances, has become an important source of water pollution.
After washing effluents are discharged into natural water, dissolved oxygen is consumed and slightly toxic to aquatic organisms, which can cause fish malformation and eutrophication caused by phosphate solvent.
If you want to know more kinds of organic membrane filters, please visit our website.
- «前のできごと |
- 次のできごと»
- このできごとのURL:


コメント